From time to time, most of us wish we could stop the clock on the ageing process, but scientists still haven’t found the key to keeping us forever young. As we get older, the body’s machinery begins to function a little less smoothly and we become susceptible to age-related and degenerative diseases. But there are certain foods that can help counteract the negative effects ageing has on the body. They won’t make you younger or stop you from getting older, but they can improve your overall health and vitality, and protect you against disease and illness, which could prolong your life and make the years you do have more healthful.
While exercise and a healthy diet can keep you fit well into old age, some foods are especially good at preventing or reducing the effects of age-related diseases and other health problems. Here we’ll look at 10 foods that pack a huge anti-ageing punch.
Skin is the largest organ in the body, so it’s certainly worthwhile taking care of. Not having an adequate diet contributes to your skin’s appearance in multiple ways. If we look at the skin’s ability to protect itself from ultraviolet light, there are key nutrients involved in that. It’s important to have vitamins A and C and D. These actually play a role in protecting skin from ultraviolet light.
How can food and nutrients reverse the ageing process?
Basically, you’re asking how do you restore elasticity to skin to give it a more supple look.
First, we have to talk about prevention. We can protect skin from ultraviolet light externally by using a sunblock. But you can do things like not smoking. Smoking damages the elastin that helps keep facial skin flexible.
Sleep is important in making sure skin gets proper rest to heal itself. Skin cells turn over at a rapid rate, and they need time to replenish and rebuild.
As for foods or nutrients that reverse ageing — vitamin A is certainly one of those, and it comes from a variety of sources. Carrots, apricots, nectarines, sweet potatoes, egg yolks, even some green things like spinach, broccoli. Collards are a great source of vitamin A.
Berries of all types
Blueberries, raspberries, cranberries, strawberries — are super rich in antioxidants, such as flavonols and anthocyanins, which promote cell health and can protect against disease. Anthocyanins in particular, found in large quantities in blackberries, are thought to help protect against cancer and diabetes.
Darker berries
Especially ones that are black or blue in color — tend to provide the best anti-ageing benefits because they have the highest concentration of antioxidants [source: Watson]. According to some studies, blueberries may even help slow or reverse neurological degeneration, improve memory, restrict the growth of cancer cells and reduce inflammation. And as an added bonus, they’re great for urinary tract health.Berries are also an excellent source of vitamins, especially vitamin C, which is good for your skin.
Double your fibre
It may help protect against cancer and can keep blood sugar levels steady and promote heart health. In fact, according to research published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, every additional 10 g of dietary fibre consumed daily reduces the risk of death from coronary heart disease by 17%. The daily recommendation is 25 to 35 g per day; most Americans eat half or less.
Eat antioxidants often,What’s the big deal about antioxidants?
“Antioxidant” is definitely a buzzword when it comes to healthy food, but what exactly does it mean? Antioxidants are substances that protect our bodies against free radicals — unstable molecules that are produced when our bodies break down food, or by exposure to pollution and radiation. Free radicals can damage our body’s healthy cells, and are thought to play a part in the onset of certain diseases, including Alzheimer’s, cancer and heart disease
Some of the most visible signs of the ageing process can be seen in our skin. Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation ages the skin more quickly. But did you know that eating (or drinking) dark chocolate has been shown to help protect the skin against the harmful effects of UV exposure?
Cocoa beans,
From which chocolate is made, have a higher antioxidant capacity than any other food, and the high concentration of antioxidant flavanols in cocoa beans helps reduce inflammation of the skin caused by exposure to UV light. Furthermore, eating dark chocolate can increase circulation in the skin and improve its ability to retain moisture, which can reduce the appearance of wrinkles and help you look younger [source: Williams].
But not all chocolate is equal when it comes to anti-ageing — it’s dark chocolate that provides the greatest benefits. That’s because the refining process involved in making other kinds of chocolate actually strips away most of the skin-benefitting antioxidant flavanols.
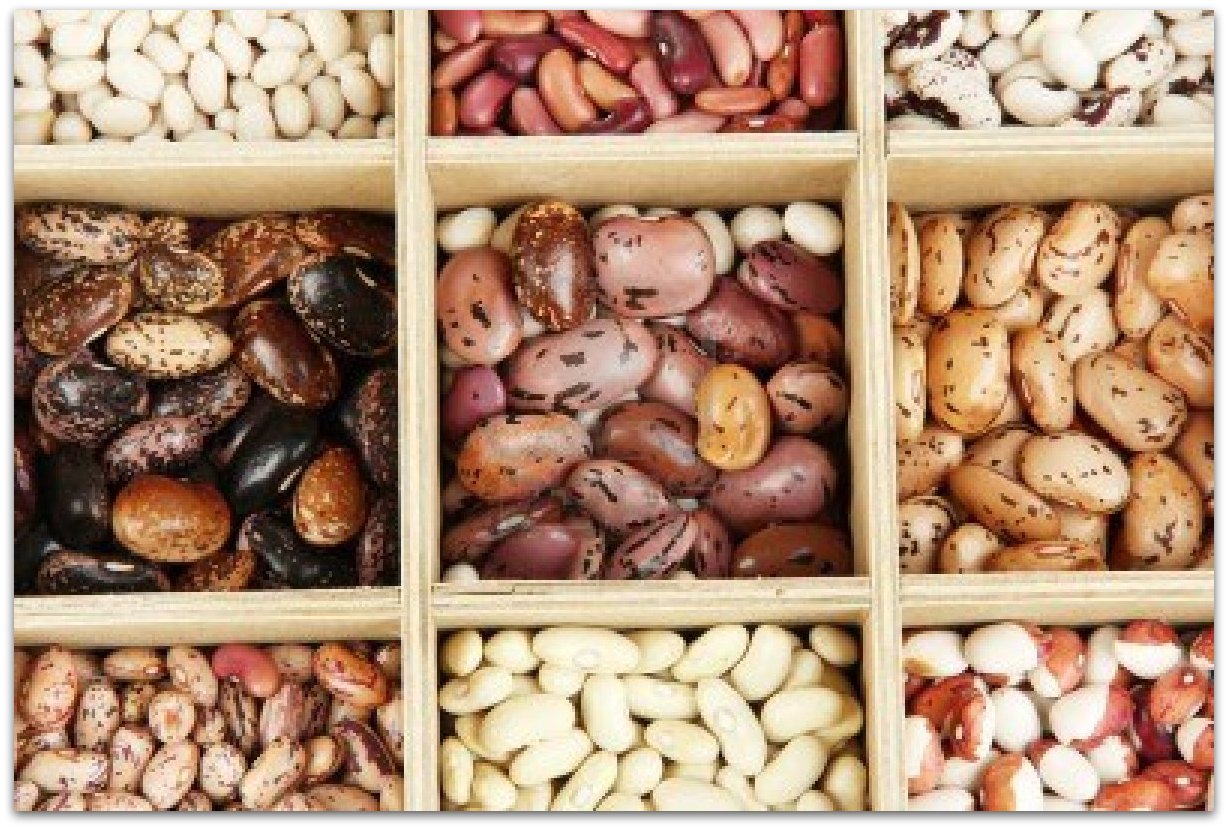
Beans–Super Foods
Beans, they’re good for your heart, the more you eat the more you, well, you get the idea. Beans often get a bad reputation because they can make you gassy, but they’re truly one of the great dietary staples. They’re an excellent source of low-fat protein, especially for those who don’t eat meat. They also contain fiber (which can help lower cholesterol), are rich in antioxidants, and are chock full of all sorts of vitamins and minerals, including iron, vitamin B and potassium.
What’s more, some beans — including soy and kidney beans — contain protease inhibitors and genistein, which are thought to help protect against cancer [source: Beare]. Studies have shown, for instance, that people who had high levels of genistein had the lowest rates of breast and prostate cancers.
Because beans have so many health benefits, they’re sometimes called a “super food” — an informal term for foods that benefit the body in many different ways. Super foods help you meet several of your dietary needs and are great sources of essential vitamins and minerals. Many also help fight disease and sickness, making them powerful anti-aging tools. Other super foods you might want to get your hands on include blueberries, yogurt, eggs, nuts, broccoli and sweet potatoes.
Fish
A popular dietary supplement in recent years has been fish oil, and there’s certainly good reason for that trend. Eating fish, or taking fish oil supplements, provides the body with omega-3 fatty acids that help protect against heart disease, reduce inflammation, decrease the risk of arrhythmia and lower blood pressure. Omega-3 fatty acids are found largely in cold-water fish, including salmon, herring, tuna and sardines.
If we are rating a food group either pro-inflammatory or anti-inflammatory, we will find that protein, on the whole, is neutral. However, some sources of protein, such as the fish listed above, provide powerful anti-inflammatory benefits for two reasons:
a. They are high anti-inflammatory omega 3 essential fatty acids which keeps skin radiant, supple and wrinkle free, moods upbeat and brain functioning at optimal levels
b. Wild salmon’s bright pink or deep red colour, depending on variety, owes its pigment to the presence of astaxanthin, a super powerful carotenoid anti-oxidant with potent anti-inflammatory properties.
Studies have even shown that people who eat a lot of fish live longer. One study of middle-aged American men found that those who ate fish two to three times per week had a 40 percent lower mortality rate than those who did not. In men who had previously suffered a heart attack, eating fish twice a week actually lowered their mortality rates by 29 percent .
Fish is also a great source of protein and, unlike other meats, is low in saturated fat. The American Heart Association recommends eating omega-3-rich fish at least two times per week.
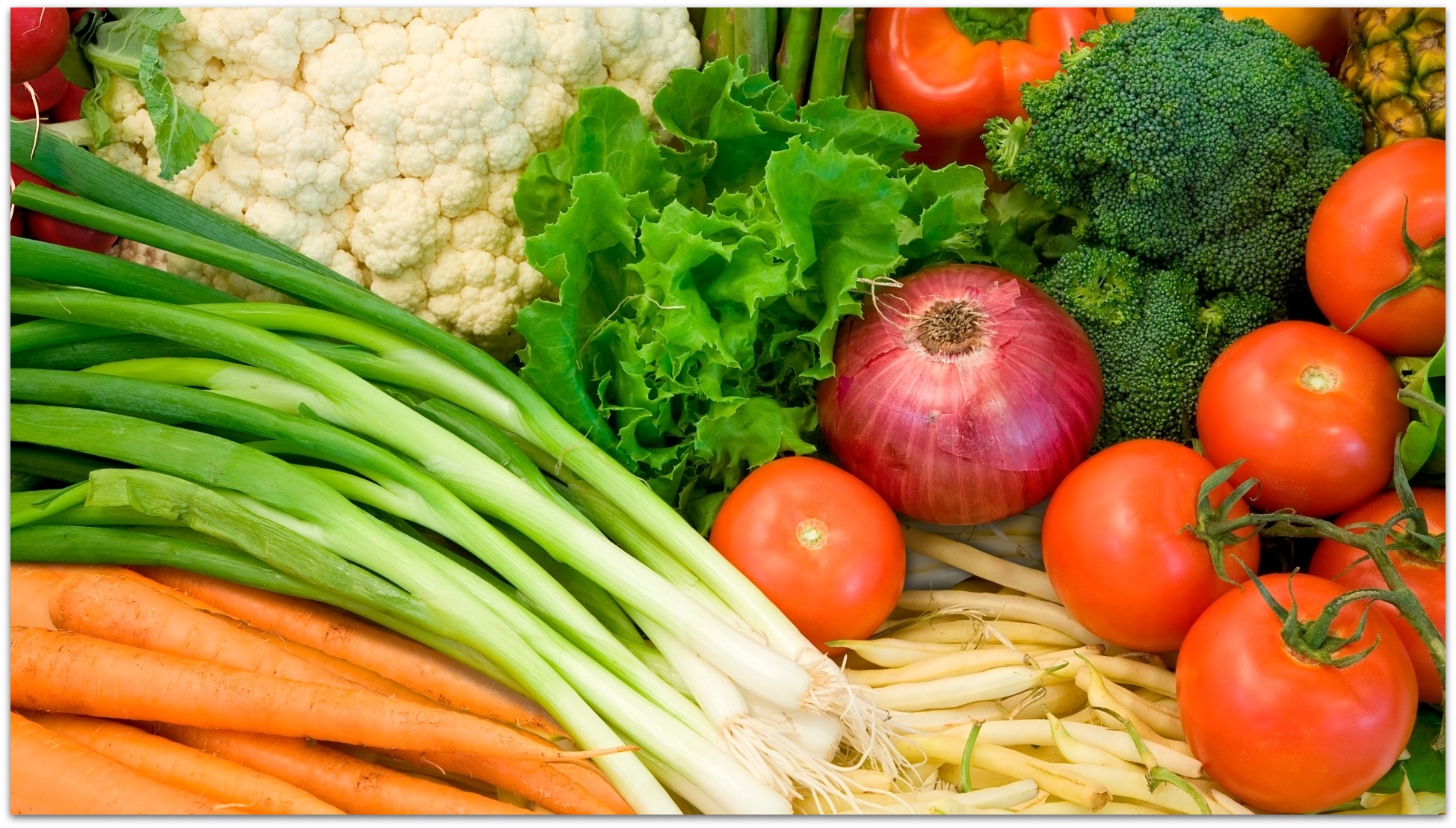
Vegetables
Are a fantastic source of vitamins and minerals, including vitamins A, C, K and E. They’re also great for the immune system, helping the body fortify itself against sickness and disease. Studies have shown that a diet full of vegetables can help prevent cardiovascular disease, lower high blood pressure and, after a heart attack or stroke, lower cholesterol and unclog arteries. Eating lots of veggies (and fruit) could even reduce the risk of cancer in the digestive tract (including the colon and stomach) by up to 25 percent.
Like fruits, vegetables are one of the best sources of antioxidants available and they can go a long way toward fighting free radicals and slowing the effects of ageing. The best vegetables for finding antioxidants are green, leafy vegetables such as spinach and kale. Two of the antioxidants found are lutin and zeaxanthin, which have also been shown to protect against the negative effects of UV exposure.
Cooked or raw?
There’s an upside and a downside to cooking vegetables before eating them. Boiling or steaming vegetables like carrots, spinach, asparagus and peppers can boost their antioxidant benefits, but it can wipe out any vitamin C they contain. Other vegetables, such as broccoli and cauliflower, are healthier raw, but cooking them can produce a compound called indole that helps kill precancerous cells .Either way you choose to eat them, veggies are good for you, so it all comes down to personal preference.
Nuts
Are known for the protein they provide, but that’s not all these small nutrient-rich foods can do for you. Nuts of all kinds are a good source of unsaturated fats. Like cold-water fish, nuts contain omega-3 fatty acids, which are great for heart health. They’re also a good source of vitamins and minerals, including potassium, which helps lower blood pressure; vitamin E, which helps prevent cell damage; and calcium to maintain strong bones.
Another great benefit of eating nuts is that they can fill you up without packing on the pounds. That’s because up to 20 percent of the calories in nuts doesn’t get absorbed by the body, making them you may have heard that drinking one glass of red wine each day is good for your heart. Well, it’s true! The antioxidants and nutrients in red wine can help prevent heart disease by protecting the arteries and the lining of blood vessels.
Red Wine
One of the most well recognized anti-ageing components found in red wine is an antioxidant called resveratrol. Studies have shown that resveratrol may help prevent blood clots, reduce the risk of cancer, decrease inflammation and lower bad cholesterol [source: Challem].
Another heart-healthy aspect of red wine is its alcohol content. Alcohol — in moderation — helps to keep blood clots from forming, increases good cholesterol and lowers bad cholesterol.
Does white wine contain resveratrol?
White wine doesn’t have as much resveratrol as red wine because resveratrol is found primarily in the skins of the grapes. The red coloring in red wine comes from the extra time the wine is in contact with the grape skins, so red wine ends up having more resveratrol than white wine. You can also get resveratrol by eating grapes and drinking grape juice. a great snack between meals [
Red Wine Has More Antioxidants Than Açaí Juice
Red wine is full of polyphenols including proanthocyanidin; a powerful antioxidant. In fact, some red wines have more antioxidants than commercial grape juice, raw blueberries and even miracle fruits like Açaí. In the fruit juice category, a full-bodied red wine will even beat pomegranate juice.
How are antioxidants measured?
Antioxidant rich foods have traditionally been measured using the ORAC method which stands for Oxygen Radical Absorbance Capacity(1). Every food has a varying ability to absorb free radicals in a controlled environment. ORAC scores range from 50 for a carrot to 5,200 for a teaspoon of cinnamon.
Red Wine vs. Antioxidant Rich Foods
- Semi-Sweet Chocolate Chips – 9,000 (1/4 cup)
- Full-Bodied Red Wine 7,700 (6 oz glass)
- Blueberries – 6,500 (1 cup)
- Pomengranate Juice – 5,500 (6 oz glass)
- Cinnamon – 5,200 (teaspoon)
- Açaí Juice – 3,030 (6 oz glass)
- Cooked Tomatoes – 1,350 (1 cup)
Why Antioxidants?
Free radicals cause destruction of our body’s cells and antioxidants stop them. Recent studies have shown antioxidants reduce the risk of some diseases, such as heart disease and cancer.
Whole Grains
It’s well known that eating whole grains is good for your digestive system — all that fiber keeps you regular and helps rid the body of unwanted substances, such as bad cholesterol and fats. Fiber also helps control your appetite and keep blood sugar low. But a diet rich in whole grains, including oats, whole wheat and brown rice, has other anti-ageing benefits because they’re rich in vitamins and minerals. Eating whole grains has also been linked to a lower risk of heart disease, stroke and diabetes
The key is to make sure the grains you’re eating aren’t refined, because it’s the refining process that strips away many of the essential vitamins and minerals that make the grains so good for you in the first place.
Garlic
Has long been thought of as a healthful and flavourful food, eaten by itself or added into a variety of delicious dishes. Its anti-ageing benefits include lowering cholesterol and blood pressure, reducing inflammation, and protecting and maintaining cell health.
One of the biggest benefits of eating garlic is that it’s a natural way to boost the immune system. Garlic has been used in folk medicine to help prevent and fight against infection for centuries, and scientific studies confirm its benefit as an anti-viral and anti-bacterial food.
Additionally, garlic has been linked to helping reduce the growth and spread of cancer cells [source: Butt]. Several studies have shown that the more garlic — both cooked and uncooked — a person eats, the lower their risk of getting stomach or intestinal cancers. It’s also been linked to reduced rates of breast and pancreatic cancers.
Garlic and Hydrogen Sulfide
Recent studies of the health benefits of garlic have pointed to hydrogen sulfide as one source of garlic’s many health benefits. Hydrogen sulfide is an antioxidant, it relaxes the arteries and promotes blood flow, and studies have even linked it to cancer defense. The body naturally produces hydrogen sulfide, but adding garlic to your diet causes your cells to produce more of this beneficial compound.
Whether you eat them in slices or mashed into guacamole, avocados are a fruit that has long been hailed for its anti-ageing properties. Avocados are a great source of vitamin E and potassium, as well as mono-unsaturated fats and antioxidants. The vitamins and minerals in avocados have been shown to reduce cholesterol, improve skin health and lower blood pressure.
The Amazing Avocado
Are also rich in folates (also called folic acid or vitamin B). Folates have been linked to heart attack prevention and reducing the risk of osteoporosis [source: Johnson]. Avocados also contain oleic acid, a mono-unsaturated fat that has been shown to lower bad cholesterol, increase good cholesterol and protect against blood clots.
What’s the only fruit that provides a wonderful source of heart-healthy fat as well as nearly 20 vitamins, minerals and phytonutrients? Avocados, of course! One fifth of a medium avocado (1 ounce) has only 50 calories, and makes a great substitute for butter, mayonnaise, or sour cream. Today, your Mount Vernon Road Hy-Vee dietitian will share tasty recipes and a new way to cut an avocado that maximizes it’s nutrition and lovely green color.
Tips for Choosing and Storing Avocados
• Avocados are ripe when they give slightly to gentle pressure with your palm. Avoid pressing with your thumb, as this can bruise the fruit.
• To hasten ripening, place avocados in a paper bag with an apple or banana for a few days at room temperature.
• Leftover ripe avocado can be stored in the refrigerator for later use. Simply mash the fruit in a covered storage container, add ½ teaspoon of lemon juice per half avocado, and lay plastic wrap over the surface. Cover container and refrigerate 2-3 days.
The New “Nick and Peel” Technique for Cutting an Avocado
The outermost layer of the avocado is dark green, and contains the highest concentration of beneficial carotenoids. Try this easy method of preparation to best preserve the nutrients and color of the fruit.
1. Wash avocado before cutting
2. Cut the avocado in half, lengthwise, around the seed.
3. Rotate ¼ turn and again cut lengthwise around the seed to make ¼ avocado segments.
4. Separate the quarters and remove the seed.
5. Starting from the tip, carefully peel each segment.
Sour Citrus Fruits,
this includes citrus like lemons, limes, and grapefruit. All are rich in antioxidants known as limonoids and limonene’s which offer their own special benefits:
I. Protect lungs; alleviate chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
II. Help prevent cancer, by boosting the activity of detoxification enzymes in the liver.
III. Lower blood cholesterol levels.
IV. Inhibit cancer in human breast cells, skin, lung, stomach, mouth and colon cancer in laboratory animals.
Lemon bioflavonoids contain hesperidin as well as proanthocyanidins. Proanthocyandins are defined as a class of nutrients that belong to the flavonoid family. A study conducted for Bordeaux Médical found that proanthocyanidins (also found in teas, black currant, bilberry, cranberry, grape seed, and grape skin) have been shown to strengthen capillaries. They also play an important role in the maintenance of elastin and the stabilization of collagen-crucial for healthy, youthful skin.
Green Tea.
Green tea contains compounds known as polyphenols which help to eliminate inflammation-producing free radicals. Recently, researchers have found that these polyphenols protect healthy cells from cancer causing DNA damage, while ushering cancer cells to their death.
Another remarkable finding is the power of green tea polyphenols known as EGCG to reactivate dying skin cells. In fact, researchers consider this amazing energizing of dying skin cells to potential benefit skin diseases such as psoriasis, ulcers, rosacea, wounds-and yes, even wrinkles.
Olives and extra virgin olive oil. We need a source of good fats in our diet, fats that will help us absorb nutrients from our vegetables and fruits, keep our cells supple, our skin glowing and wrinkle-free, our brains sharp and our mood upbeat. We also need dietary fat to burn fat. Extra virgin olive oil contains oleic acid, which helps us to absorb the omega-3s and other vitamins and nutrients from our foods. Oleic acid is vital in keeping the outer portion of the cell, known as the cell plasma membrane, supple, thereby allowing nutrients to enter the cell and wastes to exit.
The conclusion of the study was that when men were given green tea as a staple in their diet, they lost more weight and burned more calories than those who did not incorporate green tea into their diet. The health advantages of green tea are obvious for everyone to see. These processes require oxygen. Green tea is as common in today’s society as coffee and regular iced tea. The polyphenols reduce cholesterol to lower the risk of heart attack, and protect against cancer by thwarting nitrosamines that produce cancer-causing substances. Aside from green tea becoming an anti-oxidising agent it’s also claimed that it can help with cancer prevention, heart protection, rheumatoid arthritis prevention and liver protection. This is simply the inner part of the peppercorn, with the outer black skin of the fruit removed. Apparently it is a extra fat fighter. Tea has around half the caffeine of coffee, which means that it can be drunk all day long without the drinker experiencing the effects of drinking too much coffee.
Vitamin E
Vitamin E (alpha tocopherol) is a fat-soluble compound that repairs dry, cracked skin when used as a cream or lotion. This vitamin helps skin retain moisture and is often added to sunscreens because it protects the skin against UVB damage.
Vitamin E is an antioxidant that protects your body from the harmful effects of free radicals, which are molecules that have an unpaired electron. Because of this unpaired electron, free radicals seek out electrons from other cells, oxidizing them and damaging them and the tissues they form. Proper intake of vitamin E helps prevent and limit the damage caused by free radicals and oxidation. Vitamin E also improves the functioning of your immune system and assists in the expression of your genes.
Vitamin E prevents blood from clotting unnecessarily, lowering the risk of stroke or heart attack. It also helps to prevent LDL cholesterol from contributing to atherosclerosis. Vitamin E might also protect against cancer, since free radicals and their damaging effects may play a role in cancer development. However, studies into the effects of vitamin E on cancer rates are still inconclusive. Some studies even suggest vitamin E intake may put off or prevent cognitive delay or decline in the elderly due to the antioxidant effect on the brain’s neurons.
You can get vitamin E through nuts, seeds, green leafy vegetables, and vegetable oils (such as soybean, canola, and corn). Vitamin E is also available in a variety of supplements and topical applications.
Over time, no matter how careful you are, your skin is going to take on some sun damage and wear and tear. Free radicals, which are produced when you digest food or are exposed to pollution, cigarette smoke or radiation, also cause damage. Vitamin C is an antioxidant that helps prevent that damage. Not only is vitamin C an antioxidant, it helps to regenerate other antioxidants in the body, including vitamin E. When applied topically, vitamin C also helps protect your skin against the damaging effects of UV rays.
Your skin is like a blanket draped over a statue — the appearance of the outer “shell” largely depends on the shape and firmness of the structure beneath it. Collagen is the structural element of your skin that provides for shape and firmness. Vitamin C intake improves the firmness and production of collagen, giving your skin a more firm and youthful appearance. This connective tissue is also important for healing wounds.
Vitamin C
Has cancer-preventing qualities and appears to reduce the odds of developing cardiovascular disease. Additionally, some studies have suggested that vitamin C delays or even prevents the formation of age-related cataracts and macular degeneration.
Fruits and veggies (especially citrus and potatoes) are excellent natural sources of vitamin C.
Vitamin K
As you get older, dark circles may start appearing under your eyes. While they make you look tired or older than you are, these dark circles are caused by a number of factors, not just age or lack of sleep. Heredity, hormones and allergies may also be the cause (and your doctor can help you determine which).
Vitamin K helps with one common cause: the leaking of capillaries around the eyes, which results in the pooling and clotting of blood. Researchers believe that vitamin K aids in the constriction of capillaries, breaking up the tiny blood clots that form the circles. Vitamin K likely won’t be a cure-all for under-eye circles, but getting your fair share of this vitamin should be part of your treatment plan.
Your body produces small amounts of vitamin K on its own, but you can use more than your body can provide. Vitamin K can be consumed as a supplement, as part of a multi-vitamin, in the form of topical creams or (ideally) through your diet. Kale, lettuce, spinach and broccoli are all excellent sources of vitamin K, as are non-hydrogenated vegetable oils.
As we age, our bones begin to lose structural strength, due to reduced levels of ossification (an ongoing process through which bone replaces itself). Vitamin K has been shown to help ageing seniors maintain bone strength.
Niacin
Niacin, one of the B vitamins (specifically B-3), has several anti-ageing properties. One visible way it helps you as you age is by increasing your skin’s ability to retain moisture — an ability it loses over time. Moist skin not only looks healthier, it actually helps you stay healthier by providing a strong, unbroken barrier against viruses, bacteria and other antigens.
Dry skin not only can be sensitive, itchy and scaly looking, but it can also lead to further problems as the cracks between “scales” become chinks in your aging body’s armor. In addition to restoring moisture to your skin, niacin also acts like an exfoliant, helping your skin in sloughing off dead cells as newer cells move toward the surface. Dry skin can also be a result of niacin deficiency.
Niacin counteracts the effects of aging inside your skin as well. It raises your “good” cholesterol (high-density lipoproteins, or HDL) and also lowers triglycerides (fats in your blood that contribute to your overall cholesterol count). In doing so, niacin lowers your risk and rate of atherosclerosis, the hardening of your artery walls that leads to heart attack and stroke. Niacin also plays a major role in converting food into energy.
One study showed that one-fourth of all seniors don’t get enough niacin, and that number doubles for minorities and people living at or below poverty levels.
Vitamin A
Vitamin A helps you as you age in several ways. Importantly, it’s an antioxidant that helps neutralize the damaging effects of oxidation caused by free radicals. Oxidation caused by free radicals is believed to be a primary cause of age-related degeneration and disease.
Topical solutions with vitamin A (such as retinol creams) have been shown to reduce signs of sun damage and skin aging by working as an exfoliator and reducing fine lines and wrinkles. Vitamin A intake can also help with circles under the eyes, much as vitamin K does.
Vitamin A — in proper amounts — is important for your overall bone health, helping to offset the effects of osteoporosis as you get older. However, there is a danger for seniors of taking too much vitamin A, which can lead to osteoporosis and bone brittleness. Talk to your doctor about the best way for you to obtain the amount of vitamin A you need.
While vitamins aren’t going to stop you from ageing, the right ones can help slow the process down, keep you healthy late into life, and keep you looking younger than your years.
Retinol and Vitamin A
Retinol is a source of ready-to-use vitamin A. You can add it to your diet through liver, eggs and fatty fish, or in over-the-counter supplements or topical applications. Retinol has the same benefits as prescription retinoids but fewer side effects (namely sun sensitivity, redness and scaling).